By continuing to use our site, you consent to the processing of cookies, user data (location information, type and version of the OS, the type and version of the browser, the type of device and the resolution of its screen, the source of where the user came from, from which site or for what advertisement, language OS and Browser, which pages are opened and to which buttons the user presses, ip-address) for the purpose of site functioning, retargeting and statistical surveys and reviews. If you do not want your data to be processed, please leave the site.
The Voice of People With Breast Cancer
Information
Breast Cancer Basics
Breast Cancer Staging
Breast cancer staging is an important part of your pathology report and helps your healthcare team choose the best treatment for you. Staging shows how much cancer may be in your body and helps predict chances of the cancer coming back (your recurrence risk), how well treatment may work, and your overall outlook (prognosis).
Staging is based on:
- Invasiveness: Has the cancer spread beyond the milk ducts or lobules?
- Tumour size: How big is the cancer?
- Lymph node involvement: Has the cancer spread to nearby lymph nodes?
- Metastasis: Has the cancer spread to other parts of the body?
How is Staging Done?
Staging is determined through imaging tests, biopsies, and lymph node assessment. Not everyone will need every test. In many cases, lymph nodes under the arm (called axillary nodes) are removed and examined under a microscope to check for cancer cells, helping guide treatment decisions.
Common Terms in Breast Cancer Staging
- Local: Cancer is only in the breast and has not spread
- Regional: Cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes
- Distant: Cancer has spread to other parts of the body (metastatic breast cancer)
TNM Staging System
Breast cancer is staged using the TNM system, which classifies tumours based on:
-
Tumour (T): Describes tumour size and extent (T0 = no tumour, T4 = large tumour affecting skin or chest wall)
- Nodes (N): Whether the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes (N0 = no spread, N3 = spread to multiple lymph nodes)
- Metastases (M): Whether the cancer has spread to other parts of the body (M0 = no metastasis, M1 = metastasis present)
Stages range from 0 to IV based on TNM classification, for example:
- T1N0M0: Small tumour, no lymph node involvement or metastases (Stage I)
- T4N3M1: Large tumour, significant lymph node involvement, and distant spread (Stage IV)
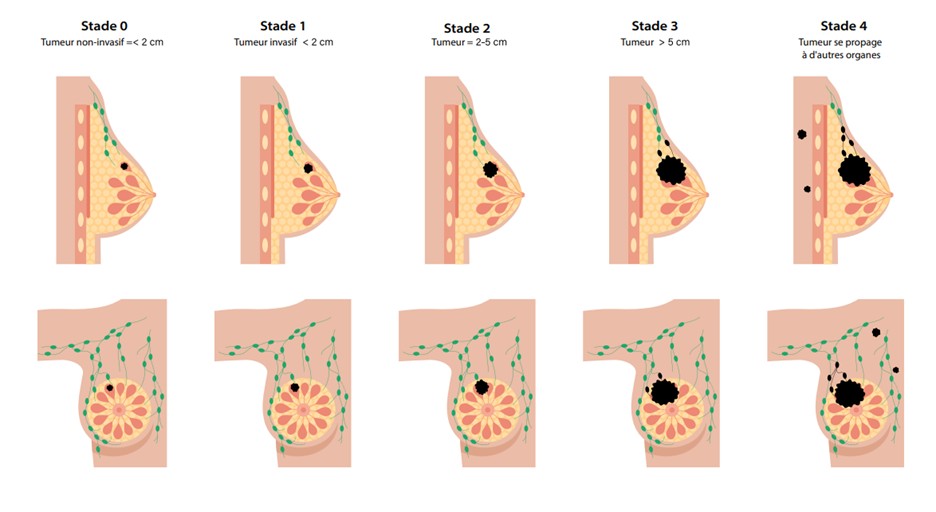
Breast Cancer Stages
-
Stage 0: Non-invasive cancer (cancer cells remain in their original location)
- Stage I: Small, localized invasive tumour that has not spread to lymph nodes
- Stage II: Larger tumour that may involve nearby lymph nodes
- Stage III: More advanced cancer with significant lymph node involvement
- Stage IV: Metastatic breast cancer (cancer has spread to distant parts of the body)
Metastatic Breast Cancer (Stage IV)
Metastatic breast cancer (also known as advanced or Stage IV breast cancer) means the cancer has spread beyond the breast to other parts of the body. About 5% of people diagnosed with breast cancer each year are first diagnosed at stage IV. Others may be diagnosed with early-stage breast cancer that later spreads. Currently, there is no national data in Canada that tracks how many people progress from early-stage to metastatic breast cancer.
How Does Cancer Spread?
Cancer can spread (metastasize) when cancer cells travel to other parts of the body. This can happen before a person is diagnosed with breast cancer (known as de novo metastatic breast cancer), or it can happen after treatment for early-stage breast cancer (known as recurrence). While breast cancer can spread anywhere, it most commonly affects the bones, lungs, liver, brain, and skin. The area where cancer has spread is called the metastatic site.
Learn More
-
Visit our Living with Metastatic Breast Cancer section to better understand your diagnosis.
- For in-depth guidance, refer to our Metastatic Breast Cancer Handbook: A Guide for Individuals Living With Stage IV Breast Cancer
- Speak with your healthcare provider if you have questions about staging or your diagnosis
Medical Review by Roochi Arora, MD, FRCPC, August 2025
- References
-
Canadian Breast Cancer Network. (2022). Breast cancer and you: A guide for people living with breast cancer [PDF]. https://cbcn.ca/web/default/files/public/
Reports/Breast%20Cancer%20and%20You_
ENG_edit_web.pdfCanadian Breast Cancer Network. (2019). Metastatic breast cancer handbook: A guide for individuals living with stage IV breast cancer [PDF]. https://cbcn.ca/web/default/files/public/
Reports/E%20-%20mBC%20Handbook.pdfJohns Hopkins Medicine. (2025). Staging and grade. https://pathology.jhu.edu/breast/staging-grade/
Lord, S. J., Bahlmann, K., O’Connell, D. L., Kiely, B. E., Daniels, B., Pearson, S. A., Beith, J., Bulsara, M. K., & Houssami, N. (2022). De novo and recurrent metastatic breast cancer - A systematic review of population-level changes in survival since 1995. eClinicalMedicine, 44, 101282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101282
Welsh, J. (2023). Stages of breast cancer: Understanding the classification system. Verywell Health. https://www.verywellhealth.com/stages-of-breast-cancer-8362458
SHARE